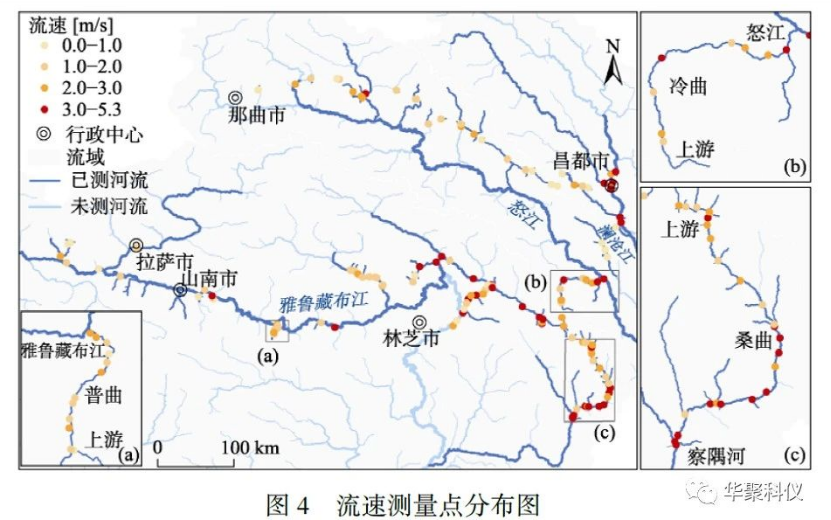
In mid-to-late June 2021 (pre-flood season), a field survey was conducted in southeastern Tibet as part of a national scientific research project led by Beijing Normal University under the Ministry of Science and Technology. Utilizing patented handheld radar flowmeters (RD-60) and outdoor rangefinders developed by Shenzhen Huaju Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd., the project team surveyed 85 rivers (including tributaries) in the region. This effort generated a dataset comprising 141 measurement points, capturing critical pre-flood environmental conditions for flood risk analysis in southeastern Tibet.

Key Findings
Based on the collected data, the study further analyzed the relationship between river flow velocity and Strahler stream order in the region. It investigated longitudinal velocity variations along the Pu Qu, Sang Qu, and Leng Qu rivers from their estuaries to headwaters, yielding significant insights. These findings enhance understanding of flood convergence patterns in southeastern Tibet and provide foundational data for flood simulation and risk mitigation strategies. The dataset has been published in the Journal of Global Change Data (Volume 6, Issue 1, 2022).
Role of RD-60 Radar Flowmeter
The RD-60 handheld radar flowmeter played a pivotal role in this survey. Designed for topographically complex and data-scarce regions like southeastern Tibet, it enabled non-contact flow velocity measurements within a 100-meter range across rivers, sewage channels, slurry flows, and marine environments. Key advantages include:
Compact design and user-friendly operation
Resistance to corrosion from polluted water and sediment interference
High-precision measurements with enhanced safety protocols

By delivering reliable flow data under challenging conditions, the RD-60 provided critical support for identifying dominant factors influencing river velocity variations in the region. This technology offers valuable references for flood disaster modeling and prevention in similar environments globally.