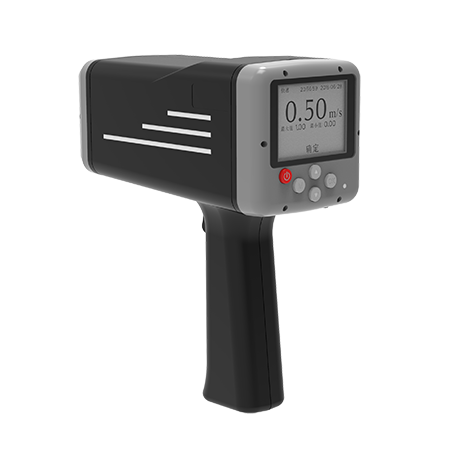
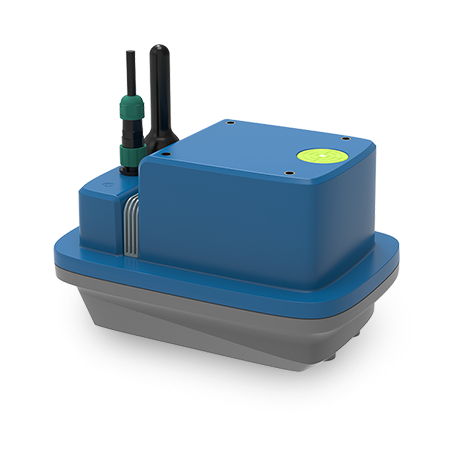
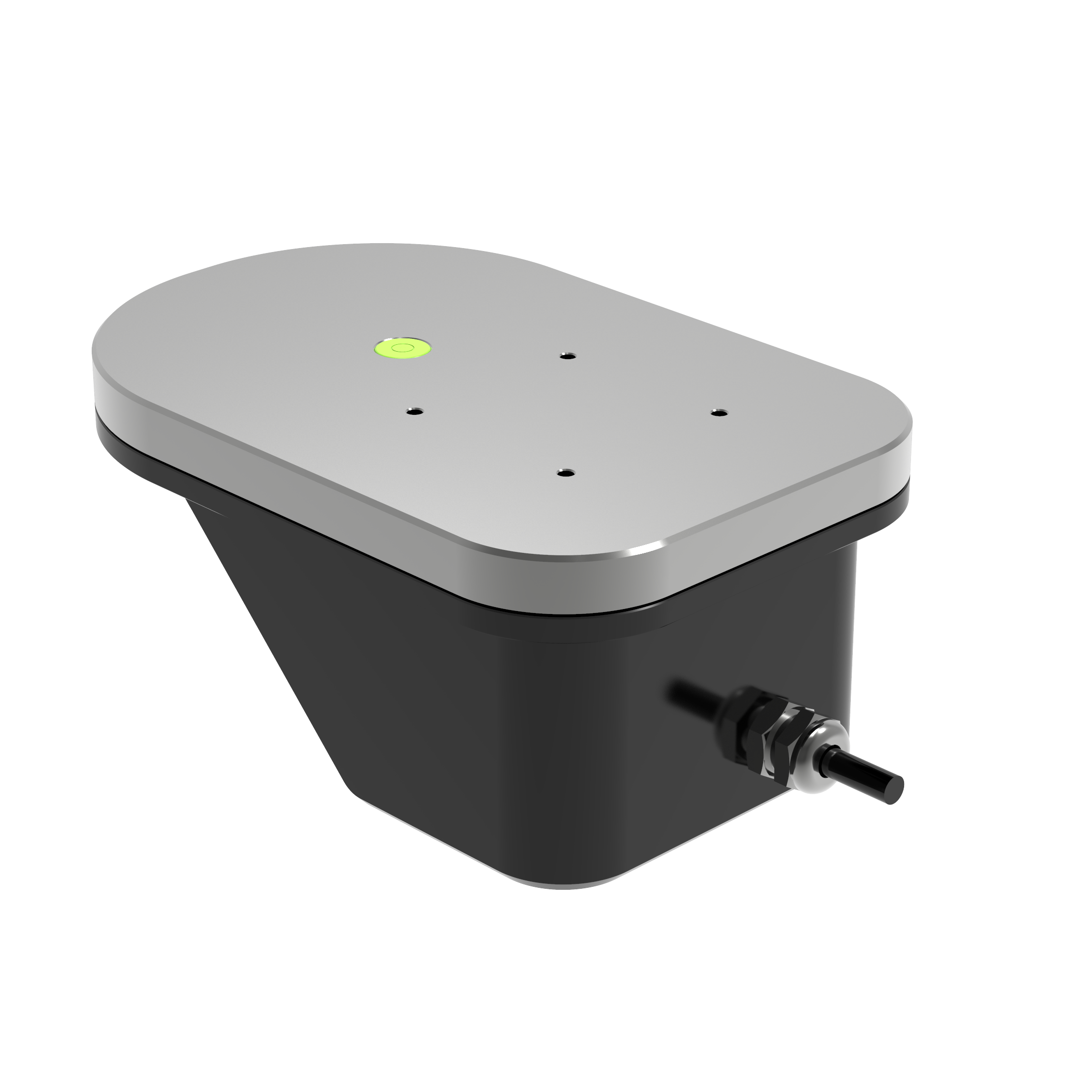
This project aims to enhance the accuracy of online water intake measurement data for 29 large and medium-sized irrigation canal intakes within the jurisdiction. Key tasks include:
Comparative calibration of online monitoring devices at intakes with active water flow.
Maintenance and debugging of monitoring equipment at intakes with no flow to ensure operational readiness.
For intakes with active flow in 2024, on-site measurements of cross-sectional shape, water level, velocity, and flow rate will be conducted. Data will be compared with online monitoring results from the provincial platform to refine calibration parameters and improve measurement accuracy.
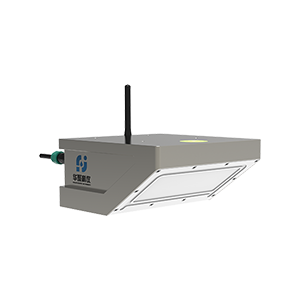
Shenzhen Huaju Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd.’s array radar flow measurement system has been deployed for its proven advantages:
Long-term reliability: Operates stably under harsh weather conditions.
Non-contact measurement: Unaffected by sediment, debris, or pollutants.
Cost-effective: Easy installation, low maintenance, and suitability for flood season monitoring.
Proven track record: Widely adopted in major irrigation districts and hydrological projects across China.
In this project, Huaju’s multi-device array radar system has been implemented to address complex flow monitoring challenges.

1.Integrated Connectivity:
2.Adaptive Zoning:
3.Non-Contact Measurement:
4.Bias Reduction:
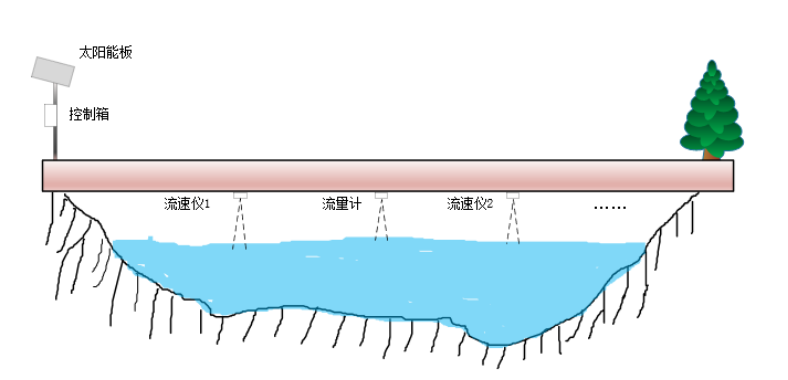
Centralized Configuration: The radar flow meter serves as the communication hub. PC-based software enables parameter setup, zone partitioning, and device configuration.
Functional Capabilities:
On-site debugging and parameter adjustment.
Cross-section data import/export.
Real-time data visualization and statistical analysis.
User permission management.
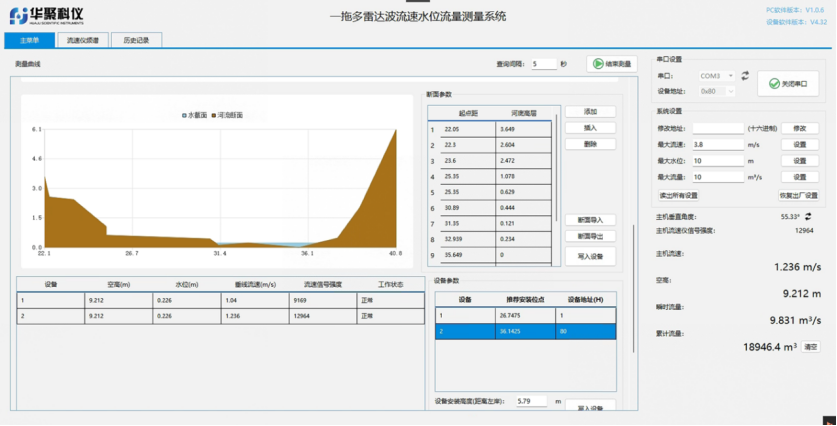
Data Collection: A server aggregates and processes water level, velocity, and flow data from the radar system.
Multi-Level Monitoring: Provincial, municipal, and county centers utilize a GIS platform to monitor all stations, enabling flow anomaly detection and early warnings.
 On-Site Application
On-Site Application